A Simple concept of unconscious
Introduction
The unconscious is one of the most complex and important concepts in psychology that has been studied and discussed since the time of Freud to the present day. In this article, we will explore the concept of the unconscious, prominent theories in this field, methods of accessing the unconscious, and its effects on behavior and decision-making. We will also mention scientific research and reliable sources in this field.
The concept of the unconscious
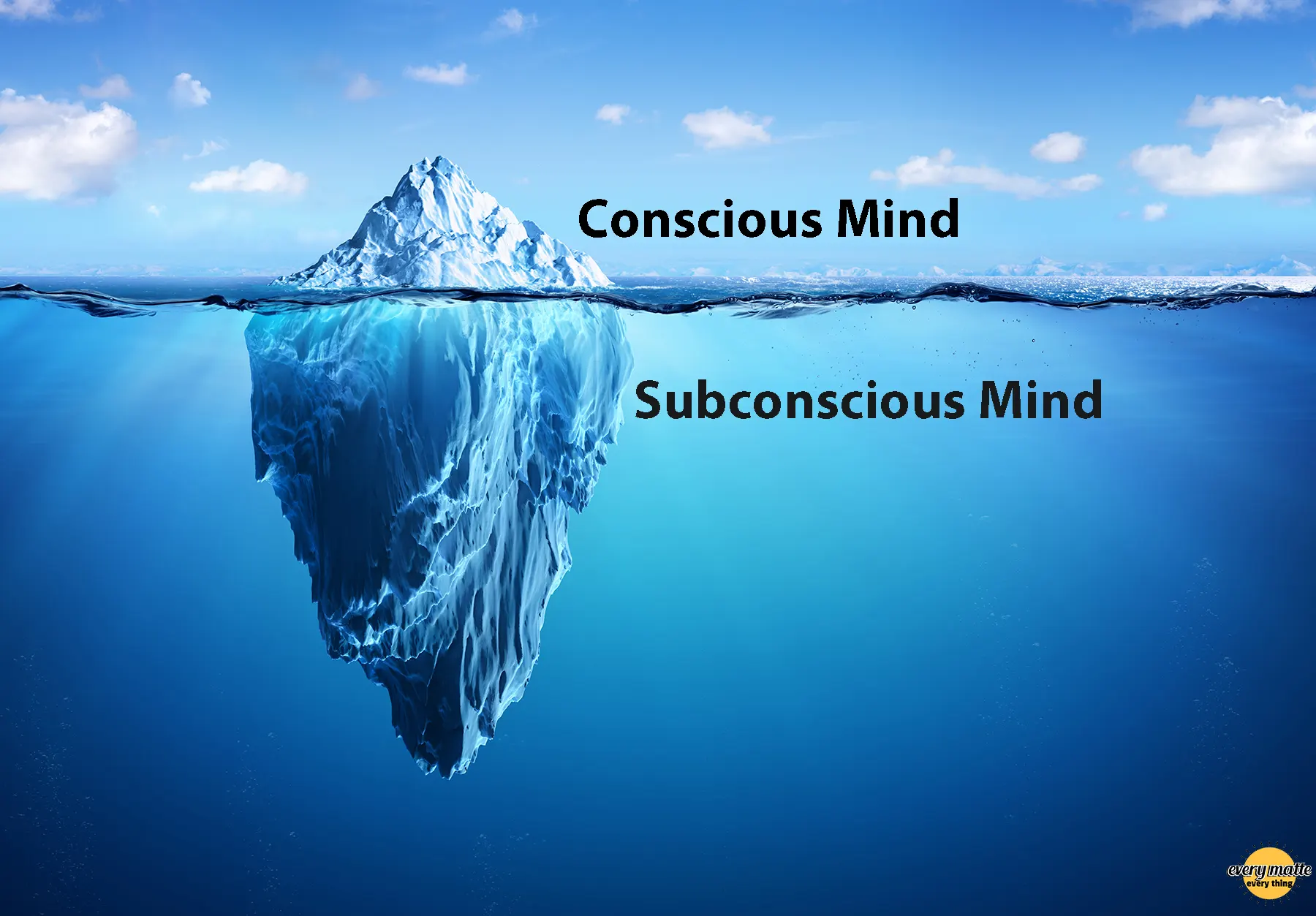
About the unconscious
The unconscious refers to the part of the human mind that contains thoughts, memories, and feelings that we do not have direct access to. This part of the mind can influence our behaviors and decisions without us realizing it ourselves (Freud, 1915).
Outstanding Comments
Freud’s theory

Freud
Sigmund Freud, the father of psychoanalysis, described the unconscious as a part of the mind that includes memories, thoughts, and tendencies that do not come to the level of consciousness due to repression or forgetfulness. He divided the human mind into three parts: the conscious, the semi-conscious, and the unconscious. Freud believed that many of our behaviors and emotions are caused by unconscious experiences and memories (Freud, 1915).
Freud’s theory of the unconscious
Sigmund Freud, the founder of psychoanalysis, is one of the most prominent theorists in the field of the unconscious. His theory of the unconscious is recognized as one of the main foundations of psychoanalysis. Freud believed that the human mind is divided into three main parts: the conscious, the semi-conscious, and the unconscious. In this part of the article, we will examine Freud’s theory of the unconscious in more detail and its effects on human behavior and psyche.
Mind-splitting
Conscious
Self-consciousness refers to the part of the mind that includes thoughts, feelings, and perceptions that are actively present in our consciousness at any given moment. This part of the mind contains all the things that we have direct access to and can think about.
Preconscious
The subconscious refers to the part of the mind that contains information that is not currently present in our consciousness, but can be easily brought to the level of consciousness. This section contains memories and information that we can access with a little effort.
Unconscious
The unconscious refers to the part of the mind that contains thoughts, memories, desires, and feelings that do not come to the level of consciousness due to repression or forgetfulness. Freud believed that the unconscious plays a very important role in shaping our behaviors and emotions. He believed that many psychological problems were caused by unconscious conflicts and experiences.
Personality Structure
Freud also divided the human personality into three parts: each of these parts plays an important role in interacting with the unconscious.
Entity (ID)
The institution is the most basic part of the personality that includes all the primitive and instinctive desires and desires of human beings. It is located entirely in the unconscious and operates on the principle of pleasure. This part of the personality seeks the immediate satisfaction of needs and desires.
Self (Ego)
It is the part of the personality that lies between the entity and the external reality. It operates on the principle of reality and strives to satisfy the needs and desires of the institution in a realistic and acceptable manner. It interacts with both the conscious and unconscious parts.
Framen (Superego)
The ego is a part of the personality that includes values, morals, and social standards. This part of the personality acts as a controlling force, trying to guide its behaviors based on moral and social principles. The meta-ego also interacts with both the conscious and unconscious parts.
Defense mechanisms
Freud believed that he himself used defense mechanisms to deal with conflicts and anxieties caused by the unconscious. These mechanisms help a person cope with unpleasant experiences and anxieties caused by internal conflicts. Some of the defense mechanisms include:
Repression
Suppression is one of the main defense mechanisms in which unpleasant thoughts, memories, and tendencies are pushed into the unconscious and out of the reach of the conscious.
Denial
In denial, the person does not accept unpleasant realities and is removed from their consciousness.
Displacement
In displacement, the person shifts their feelings or desires from a primary goal to an alternative, less threatening one.
Sublimation
In sublimation, the person transforms their unconscious desires into social, cultural, or artistic activities that are accepted by society.
Psychoanalysis
Freud used different methods known as psychoanalysis to access the unconscious and investigate internal conflicts. Some of these methods include:
Free Association
In this method, the person is encouraged to express whatever comes to his mind without any restrictions. This process can help uncover unconscious thoughts and tendencies.
Dream Analysis
Freud believed that dreams were a way to access the unconscious. He believed that dreams symbolically represent unconscious desires and conflicts.
Slips of the tongue (Freudian Slips)
Freud believed that language slips (referred to as unintentional speech mistakes) could represent unconscious thoughts and tendencies.
But in the end…
Freud’s theory of the unconscious is one of the most influential theories in psychology that has had profound effects on our understanding of the human mind and behavior. Although some aspects of Freud’s theory have been criticized, its basic principles are still used and studied in modern psychology. Continued research in this field can lead to a better and more complete understanding of the unconscious and its effects on human behavior and psyche.
Jung’s theory

Jung’s theory
Carl Gustav Jung, one of Freud’s students, referred to the collective unconscious in addition to the personal unconscious. Jung believed that this part of the unconscious includes experiences and symbols shared by all human beings. He called these symbols “archetypes” (Jung, 1968).
Carl Jung’s theory of the unconscious
Carl Gustav Jung, one of the most prominent psychologists and founders of analytical psychology, has proposed very important theories in the field of the unconscious. Jung’s theory of the unconscious differs significantly from that of Sigmund Freud and deals with deeper and broader aspects of the human mind. In this part of the article, we will examine Jung’s theory of the unconscious and the key concepts related to it.
Unconscious segmentation
Jung believed that the unconscious is divided into two main parts: the personal unconscious and the collective unconscious.
Personal Unconscious
The personal unconscious includes all the experiences, memories, and feelings that a person does not bring to the level of consciousness for various reasons. This part of the unconscious includes all the things that a person has pushed into the unconscious due to repression, forgetfulness, or lack of attention. The personal unconscious is similar to the concept that Freud had proposed of the unconscious.
Collective Unconscious
It is one of the key and unique concepts in Jung’s theory. He believed that in addition to the personal unconscious, each individual has a collective unconscious that includes the shared experiences and knowledge of humans as a species. This part of the unconscious consists of archetypes patterns and images that have been repeated throughout history and cultures.
Archetypes
Archetypes are primitive and universal patterns and images that exist in the collective unconscious and appear in different forms in different cultures and mythologies. Some of the important archetypes in Jung’s theory are:
Self
Archetype itself refers to the integrity and integrity of the personality. This archetype represents the complete realization of individuality and the balance between different aspects of personality.
Shadow
The shadow represents the darker and more unpleasant aspects of the personality that the person tends to suppress or deny. This archetype includes desires and feelings that conflict with the social and moral standards of the individual.
Anima and Animus
They represent the feminine and masculine aspects in the subconscious of each individual. The anima represents the feminine aspects in men and the animus represents the masculine aspects in women. These archetypes contribute to the balance and psychological development of the person.
Wise Old Man and Great Mother
These archetypes represent the wise and supportive aspects of the collective unconscious. The wise old represents wisdom and deep knowledge, and the grandmother represents support, affection, and spiritual nourishment.
The process of individuation
Jung believed that the main goal of a person’s psychic life is the process of individuality, which means the full realization and integrity of personality. This process involves recognizing and accepting various aspects of personality, including archetypes and unconscious aspects. Individuality helps one achieve balance and harmony between different aspects of personality and achieve full self-realization.
Methods of accessing the unconscious
Jung used a variety of methods to access the unconscious and examine archetypes and internal conflicts. Some of these methods include:
Dream Analysis
Jung believed that dreams were a way to access the collective unconscious and archetypes. He believed that dreams could convey messages from the collective unconscious and shared experiences of human beings to the individual.
Active Imagination
Active imagination is the way in which a person actively interacts with their unconscious images and patterns. This method can help a person become familiar with and understand archetypes and aspects of their subconscious.
Symbol Analysis
Jung believed that symbols and images in art, mythology, and cultures could represent archetypes and collective unconscious experiences. Symbol analysis can help one gain a deeper understanding of the collective unconscious.
Carl Jung’s theory of the unconscious is one of the most prominent and influential theories in analytical psychology that examines deeper and broader aspects of the human mind. Key concepts such as the collective unconscious, archetypes, and the process of individuality contribute to a better and more complete understanding of the human psyche. Continued research in this field can lead to the development and evolution of Jung’s theories and a better understanding of the unconscious and its effects on human behavior and psyche.
Methods of accessing the unconscious

Psychotherapy
Different psychotherapy modalities help people access their subconscious and identify and change unconscious patterns. It can help to improve psychological problems and increase one’s awareness (Freud, 1915).
Methods of accessing the unconscious in psychotherapy
Access to the unconscious is an important aspect of psychotherapy that helps therapists reach the deeper roots of patients’ psychological and emotional problems. There are different ways to access the unconscious, each of which can contribute to better cognition and more effective treatment. In this section, we will explore some of these methods.
1. Dream Analysis
One of the popular methods in psychotherapy to access the unconscious is dream analysis. Both Freud and Jung used this method, but with different approaches.
Freud’s Approach:** Freud believed that dreams represent repressed desires and desires. He used dream analysis to explore these tendencies and examine internal conflicts.
Jung’s Approach:** Jung believed that dreams could convey messages from the collective unconscious and archetypes to the individual. He saw dreams as a way to access common experiences and knowledge of human beings.
2. Active Imagination
Active imagination is the way in which a person actively interacts with their unconscious images and patterns. This method involves focusing on mental images and allowing them to evolve and change. Active imagination can help a person become familiar with and understand archetypes and aspects of their unconscious.
3. Free Association
Free association is one of the main methods in Freudian psychoanalysis, which allows the person to talk about anything that comes to their mind without restrictions. This method can help uncover repressed thoughts and feelings and internal conflicts.
4. Symbol Analysis
Symbol analysis is a method in which the therapist examines symbols and images in dreams, art, mythology, and cultures. These symbols can represent archetypes and collective unconscious experiences. Symbol analysis can help to better and deeper understand the collective unconscious and its effects on the individual psyche.
5. Hypnosis
Hypnosis is one of the oldest and most effective ways to access the unconscious. In this procedure, the person enters a transhypnotic state in which the conscious mind is reduced and the unconscious mind becomes more active. This method can help uncover repressed experiences and change behavior patterns.
6. Art and Creative Techniques
Using art and creativity can be an effective way to access the unconscious. Painting, sculpture, creative writing, and music can help a person express their unconscious feelings and thoughts and gain a better understanding of them.
!!!
There are different ways to access the unconscious in psychotherapy, each of which can contribute to better cognition and more effective treatment. Dream analysis, active imagination, free association, symbol analysis, hypnosis, and artistic and creative techniques are among these methods. Using these methods can help therapists get to the deeper roots of patients’ psychological and emotional problems and help them in the process of personal recovery and growth.
Hypnosis is one of the ways of accessing the unconscious in which the person is placed in an altered state of consciousness. This state can help a person communicate with the unconscious parts of their mind (Hilgard, 1977).
Hypnosis
Hypnosis is a psychotherapeutic technique in which the person enters a transhypnotic state. In this case, the person’s conscious mind decreases and the unconscious mind becomes more active, so that the person becomes more sensitive and receptive to the therapist’s suggestions. Hypnosis can help uncover repressed experiences and change behavior patterns.
History of Hypnosis
Hypnosis has been used since ancient times. In the 19th century, the Austrian physician, Franz Anton Mesmer, used hypnosis as a therapeutic method and called it “mesmerism.” Later, the Scottish physician James Beard coined the term “hypnosis” and began to study this phenomenon scientifically.
Stages of Hypnosis
Hypnosis is usually performed in several stages:
1. Preparation:** In this stage, the therapist talks to the person and prepares them to enter the trans state. It consists of building trust and peace of mind in the person.
2. **Induction:** The therapist uses a variety of techniques, such as focusing on an object, breathing deeply, or using calming words to induce a trans state.
3. **Deepening:** After entering the trans state, the therapist uses deepening techniques to bring the person into a deeper trans state.
4. Therapeutic Suggestions:** In this stage, the therapist offers the person his or her treatment suggestions. These suggestions can include changing behavior patterns, reducing stress, or exploring repressed experiences.
5. **Awakening:** Eventually, the therapist returns the person to a state of awakening and brings him out of the trans state.
Applications of Hypnosis
Hypnosis is used in a variety of cases, including:
Anxiety and Stress Treatment: Hypnosis can help reduce anxiety and stress and make a person more relaxed.
Treatment of phobias: Hypnosis can help a person deal with their irrational fears and reduce them.
Pain Management: Hypnosis can help reduce chronic pain and manage acute pain.
Quitting bad habits: Hypnosis can help a person quit bad habits such as smoking or overeating.
Improved sleep: Hypnosis can help improve sleep quality and reduce sleep problems.
Safety and Side Effects
Hypnosis is generally safe and has no serious side effects. However, some people may not respond to hypnosis or feel uncomfortable in a trans state. In rare cases, hypnosis can cause false memories. For this reason, it is important that hypnosis is performed by an experienced and certified therapist.
!!!
Hypnosis is a powerful tool in psychotherapy that can help uncover repressed experiences and change behavior patterns. This method is especially effective in treating anxiety, stress, phobias, pain management, quitting bad habits, and improving sleep. However, the use of hypnosis must be performed by an experienced and accredited therapist to ensure its safety and effectiveness.
Lucid dreaming, or “Lucid Dreaming,” is a state in which a person becomes aware that they are dreaming while sleeping. This state can help a person access and interact with their subconscious (LaBerge, 1985).
Lucid Dreams
Lucid dreams, or lucid dreams, are a state of sleep in which a person is aware that they are dreaming and can control the contents of the dream. This can be a very interesting and useful experience and help people cope better with their psychological and emotional issues.
Characteristics of lucid dreams
1. Awareness of being asleep: A person knows that he is dreaming.
2. **Dream Control:** A person can influence the content of the dream and what happens in it.
3. High Clarity and Detail:** Lucid dreams usually have more clarity and detail than normal dreams.
Ways to Achieve Lucid Dreams
To experience lucid dreams, several techniques can be used:
1. Reality Testing:** Throughout the day, regularly ask yourself if you’re dreaming. This will help you to continue this habit while you sleep and thus become aware of your dreams.
2. **Dream Journaling:** Keep a dream journal and write down your dreams in it every morning. This will help you remember your dreams better and identify recurring patterns.
Wake Back to Bed (WBTB):* In this technique, you wake up in the middle of the night and stay awake for a while, then fall back asleep. This can increase the likelihood of experiencing lucid dreams.
4. Mnemonic Induction of Lucid Dreams (MILD):* Before you go to sleep, tell yourself that you will be aware in your next dream that you are dreaming. This technique will help strengthen your intention to experience lucid dreams.
5. Meditation and relaxation techniques: Meditation and relaxation practices can help you prepare your mind to experience lucid dreams.
Applications of lucid dreams
Lucid dreams can have several uses:
1. Solving psychological and emotional issues: By controlling lucid dreams, you can face your fears and worries and manage them better.
2. Increased Creativity:** Lucid dreams can help you come up with creative ideas and see things from new angles.
3. Practice Skills:** In lucid dreams, you can practice a variety of skills, such as playing a musical instrument or performing a sporting move.
4. **Adventurous Experiences:** Lucid dreams allow you to experience the adventurous and impossible, such as flying or exploring imaginary worlds.
Safety and Considerations
Lucid dreams are generally safe, but some people may have unpleasant experiences, such as sleep paralysis or lucid nightmares. If these problems arise for you, you can manage these problems by cutting back on lucid dreaming practices and focusing on relaxation and meditation techniques.
!!!
Lucid dreams are a fascinating and useful phenomenon in psychology and self-knowledge that can help people cope better with their psychological and emotional issues, increase their creativity, and have adventurous experiences in the dream world. By using various techniques, lucid dreams can be achieved and the benefits can be reaped.
Unconscious Influences on Behavior and Decision-Making
Research has shown that many brain processes are carried out unconsciously. For example, when we make a decision, our brain may have made that decision before we became aware of it ourselves (Libet, 1985). Also, the unconscious can have profound effects on our social, emotional, and cognitive behaviors (Bargh & Chartrand, 1999).
Unconscious Influences on Behavior and Decision-Making
The unconscious is the part of the mind that operates outside of our conscious consciousness and plays a very important role in shaping our behaviors and decisions. This part of our mind contains thoughts, feelings, memories, and impulses that operate automatically without our conscious awareness.
The role of the unconscious in behavior
1. Automated Habits and Behaviors: Many of our everyday behaviors, such as driving, brushing our teeth, or typing, are done automatically without the need for conscious thinking. These behaviors are stored in our subconscious and help us devote our mental energy to more complex issues.
2. Emotional Responses: Our unconscious plays a big role in shaping emotional responses. For example, we may feel scared or happy when faced with a particular situation without consciously knowing why. These responses may be caused by past experiences or emotional patterns stored in the unconscious.
3. Prejudices and prejudices: Many of our prejudices and prejudices also operate on an unconscious level. These biases can influence our decision-making, causing us to act unconsciously in favor of or against a certain individual or group.
The role of the unconscious in decision-making
1. Quick and intuitive decision-making: Our subconscious can play an important role in making quick and intuitive decisions. These types of decisions are usually based on past experiences and patterns stored in the subconscious and can be very useful in emergency and complex situations.
2. Unconscious Influences on Choices: Studies have shown that many of our choices are influenced by unconscious factors. For example, ads can subconsciously influence our preferences and encourage us to buy a particular product.
3. Creative Problem Solving: Our subconscious can play an important role in the process of solving creative problems. Many creative and innovative ideas may come out of our subconscious when we are not consciously thinking about the problem.
Techniques for exploiting the unconscious
To harness the power of the unconscious and improve behaviors and decision-making, several techniques can be used:
1. Meditation and Relaxation: Meditation and relaxation practices can help you access your subconscious and use it to improve your behaviors and decisions.
2. Psychotherapy: Psychotherapy techniques such as hypnotherapy and psychoanalysis can help you access your subconscious and better manage your psychological and emotional issues.
Self-knowledge techniques: Self-knowledge exercises such as journaling and analyzing dreams can help you get to know your subconscious better and use it to improve your behaviors and decisions.
!!!
The unconscious plays a very important role in shaping our behaviors and decisions. By exploiting various techniques, the unconscious can be accessed and used to improve behaviors, make decisions, and solve creative problems. Knowing and understanding the unconscious better can help us live a better life and cope better with our psychological and emotional issues.
Scientific research on the effects of the unconscious on behavior and decision-making
There has been a lot of scientific research on the unconscious influences on behavior and decision-making, which shows that this part of the mind plays a very important role in our daily lives. Here are some of the most important research and scientific findings in this field.
1. **Unconscious prejudices and prejudices**
Studies have shown that unconscious prejudices and biases can significantly influence our decisions and behaviors. One of the most popular tools for measuring these biases is the Implicit Association Test, developed by researchers at Harvard University. This test suggests that individuals may unconsciously have biases towards different groups that influence their social behaviors and decision-making.
2. **Intuitive Decisions**
In their research, Daniel Kahneman and Amos Twersky have shown that intuitive and quick decisions are usually made based on past experiences and patterns stored in the unconscious. These types of decisions, also known as “System 1”, can be very useful in emergency and complex situations. Kahneman has discussed this topic in detail in his book “Thinking, Fast and Slow.”
3. **Unconscious Influences on Consumers’ Choices**
Research in the field of marketing has shown that advertising and branding can unconsciously influence consumers’ preferences and choices. For example, studies conducted by Gerald Zaltman show that up to 95 percent of our purchasing decisions are influenced by unconscious factors. These findings highlight how marketers can use different techniques to influence consumers’ subconscious.
4. **Creative Problem Solving**
Research shows that the unconscious plays an important role in the creative problem-solving process. For example, studies conducted by Mihaly Tsikszentmihai show that states of mind such as “Flow”, in which a person is fully immersed in an activity, can help increase creativity and innovation. In these states, the unconscious actively participates in solving problems and generating new ideas.
5. **Neuroscience Research**
Research in neuroscience has also shown that different parts of the brain are involved in unconscious processes. For example, studies using brain imaging show that parts of the brain such as the amygdala and hippocampus are involved in processing emotional information and unconscious memories. These findings help us better understand how the unconscious can influence our behaviors and decisions.
!!!
Scientific research shows that the unconscious plays a very important role in shaping our behaviors and decisions. From unconscious prejudices and prejudices to intuitive decision-making and creative problem-solving, the unconscious actively participates in our daily lives. By better understanding this part of the mind and exploiting various techniques, we can improve our behaviors and decision-making and live a better life.
Neuroscience
In neuroscience, research has shown that many brain processes are carried out unconsciously. For example, brain activities related to decision-making and information processing take place in the unconscious before they reach the conscious level (Libet, 1985).
Experimental Psychology
In experimental psychology, various studies have investigated the effects of the unconscious on behavior and decision-making. These studies have shown that many of our behaviors and decisions are influenced by unconscious processes (Bargh & Chartrand, 1999).
Resources
1. Freud, S. (1915). The Unconscious. Standard Edition, 14, 159-215.
2. Jung, C. G. (1968). The Archetypes and The Collective Unconscious. Princeton University Press.
3. Hilgard, E. R. (1977). Divided Consciousness: Multiple Controls in Human Thought and Action. Wiley-Interscience.
4. LaBerge, S. (1985). Lucid Dreaming. Ballantine Books.
5. Libet, B. (1985). Unconscious cerebral initiative and the role of conscious will in voluntary action. Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 8(4), 529-566.
6. Bargh, J. A., & Chartrand, T. L. (1999). The Unbearable Automaticity of Being. American Psychologist, 54(7), 462-479.
!!!
The unconscious is one of the key and complex concepts in psychology that has profound effects on human behavior and decision-making. Despite extensive research and various theories, many aspects of the unconscious still remain unknown. Continued research in this field can lead to a better and more complete understanding of the human mind.


